Laterite nickel ore related knowledge
I. Overview of nickel ore
At present, it has been proven nickel resource on the land, the nickel-metal industrial reserves of about eighty million tons, nickel sulphide minerals mainly nickel and nickel laterite ore (also known as laterite nickel ore) exists in two forms, which Nickel sulphide ore accounts for about 20%, nickel laterite ore for about 75%, and nickel silicate ore for 5%. The development and utilization of nickel ore is mainly for nickel sulphide or nickel laterite ore, mainly producing nickel countries Canada, Russia, Australia, New Caledonia, Indonesia, Philippines, Cuba, China.
(1) Nickel sulfide ore
Nickel sulfide ore pyrite mainly nickel (Fe, Ni) 9 S 8 , purple sulfur pentlandite (Ni 2 FeS 4), the free needle nickel sulfide (of NiS) nickel, present form, a considerable portion of the nickel to the quality class The same image is present in the pyrrhotite. According to the nickel content, the primary nickel ore can be divided into three grades:
Tefu Mine: Ni≥3%, rich ore: 1%≤Ni≤3%, lean ore: 0.3%≤Ni≤1%
1. Distribution of nickel sulfide ore
Canada: Sudbury Nickel Belt, Lin Lake-Thompson Nickel Belt;
Russia: Kola Peninsula Nickel Belt, Siberian Norris Nickel Mine;
Australia: Kambada Nickel Mine
China: Jinchuan Nickel Belt, Jilin Yanshi Nickel Belt
Finland: Kotalati Nickel Belt
2. Beneficiation treatment of nickel sulfide ore
Most of the original nickel sulphide ore has a nickel content of less than 3%, and for nickel sulphide ore with a nickel content of 0.3-1%, it needs to be beneficiated. Nickel sulfide ore containing copper, nickel, the presence of free sulphide predominantly pentlandite, needle sulfur nickel ore, nickel, nickel purple sulfur forms, such nickel sulfide mine butyl or pentyl and the like to use advanced active xanthate Flotation. The nickel concentrate after flotation can be divided into nickel with a nickel content ranging from 3% to 8%, with a difference of 0.5%. There are 11 levels:
Special grade Ni≥8%, first grade 7.5%≤Ni≤8%......
Nine grade products 3.5% ≤ Ni ≤ 4% tens of grade 3% ≤ Ni ≤ 3.5%
3. Nickel sulfide ore extraction method
Nickel sulphide ore (flotation)----nickel concentrate (blast furnace smelting)----low ice nickel (converter blowing)----high ice nickel (plus sulfuric acid at normal pressure, high pressure leaching)----nickel sulfate (Electrolysis) --- Electrolytic nickel.
(2) Nickel laterite ore
Nickel oxide ore, a high nickel laterite ore containing iron, low silicon-magnesium, nickel 1% to 2%; low nickel silicate as iron, high stevensite-containing, nickel 1.6% to 4.0%. At present, the development and utilization of nickel oxide ore is mainly nickel laterite ore, which is developed from the weathering of ultrabasic rocks. Nickel is mainly in the form of nickel limonite (rarely crystallized to non-crystalline iron oxide).
1. Distribution of nickel laterite ore:
New Caledonia Nickel Belt
Indonesia: Molujia Nickel Belt, Sulawesi Nickel Belt;
Philippines: Nickel Belt in Palawan;
Australia: Queensland Nickel Belt;
Brazil: Minas Gerais Nickel Belt, Goias Nickel Belt;
Cuba: Orient Nickel Belt
2. Treatment method of nickel laterite ore:
Nickel in nickel laterite ore is often dispersed in gangue minerals with the same type of similarity, and the particle size is very fine and has a certain viscosity. It is difficult to obtain good effect by direct treatment by mechanical beneficiation method. After the ore is changed by roasting to change the mineral structure, Good technical indicators can be obtained, but the cost is high and has not been used in industrial production. Due to the continuous increase of nickel consumption and the reduction of nickel sulfide ore reserves in recent years, the development of nickel laterite ore has been paid more and more attention. At present, nickel laterite ore is directly smelted ore, and the smelting method can be basically divided into wet method and fire method. Big category:
Wet method 1: primary nickel oxide ore (high-pressure leaching with sulfuric acid)-----nickel sulfate (adding precipitant hydrogen sulfide)-----nickel sulfide (NiS)
Wet method 2: primary nickel oxide ore (reduction and burning) ---- Nickel in the ore is in the form of nickel-iron alloy (added ammonia solution) - nickel hexammine complex (rotary kiln drying and calcination) )-----nickel oxide powder (reduction reaction) - metal nickel.
Fire method 1: primary nickel oxide ore (rotary kiln drying, electric furnace smelting) ------ ferronickel.
Fire method 2: primary nickel oxide ore (sintering machine sintering, blast furnace smelting) ------- nickel-iron alloy.
The difference between Fire Method 1 and Fire Method 2 is that Fire Method 1 needs to consume a large amount of electric energy, and the cost is high. It is suitable for treating nickel oxide ore with a nickel content of 1.5% or more, while Fire Method 2 uses coal and coke as raw materials, and the cost is relatively high. It is suitable for the treatment of ore with a nickel content of 0.8-1.5%. At present, the most fundamental reason why the fire method 2 is widely used is that it can utilize the relatively low-grade primary nickel oxide ore, effectively alleviating the serious shortage of nickel ore resources. situation.
Second, the situation of laterite nickel ore
(1) Classification
Nickel oxide ore is basically divided into two categories, one is laterite nickel ore, the other is nickel silicate ore, the upper part of the deposit, due to weathering and leaching results, more iron, less silicon, less magnesium, lower nickel The lower part of the deposit, due to weathering enrichment, nickel ore, polysilicon, magnesium, low iron, high nickel, called magnesium nickel silicate;
(2) Metallogenic characteristics:
Nickel laterite ore is usually divided into three levels.
First layer: Lateritic Nickel Ore ( laterite nickel ore)
Ni 0.9-1.1% Fe 45-50%
Second layer: Limonitic Nickel Ore (nickel limonite)
Ni 1.4-1.9% Fe 20%-30%
Third floor: Saprolite Nickel Ore (soiled nickel mine)
Ni 2.0-2.6% Fe 15% or so
Laterite nickel ore metallogenic map

(3) Mining methods
The laterite nickel mine is open-pit mining and has simple operation equipment. It usually consists of the following steps:
1. Bulldozer cleaning and stripping the soil
2. Simultaneous testing of mineral components in mining
3. Stacking minerals according to the test results
(4) Use
The nickel content of different mineral layers is also different. Nickel ore with different nickel content has different uses. The laterite nickel ore with nickel content of 0.8-1.5% is mainly used for smelting nickel-iron alloy in blast furnace. The Ni content of the alloy is 1.6-4.0%; the nickel content is 1.5- 2.6% of laterite nickel ore is mainly used for the production of ferronickel with a Ni content of 10-30%.
GF1 Diesel Generator Suppliers
Brief Induction
1) 3-24kw Series of ordinary diesel generating sets have been provided with high quality water-cooled diesel engine, those engine can work well in every kinds of conditions2) The structure of generating sets, the engine has been coupled with alternator through v-belt or coupled directly with alternator, both of them have been installed on the basis of anti-shock pad, The gen-sets have been fixed on the frame of shock pipes which has four wheels.
3) Other features It's easy to operate and maintain, control panel, capacitor type, voltage regulator, no-fuse circuit breaker, over-current protection, wheels type design, double-shaft balance design, electric starting.
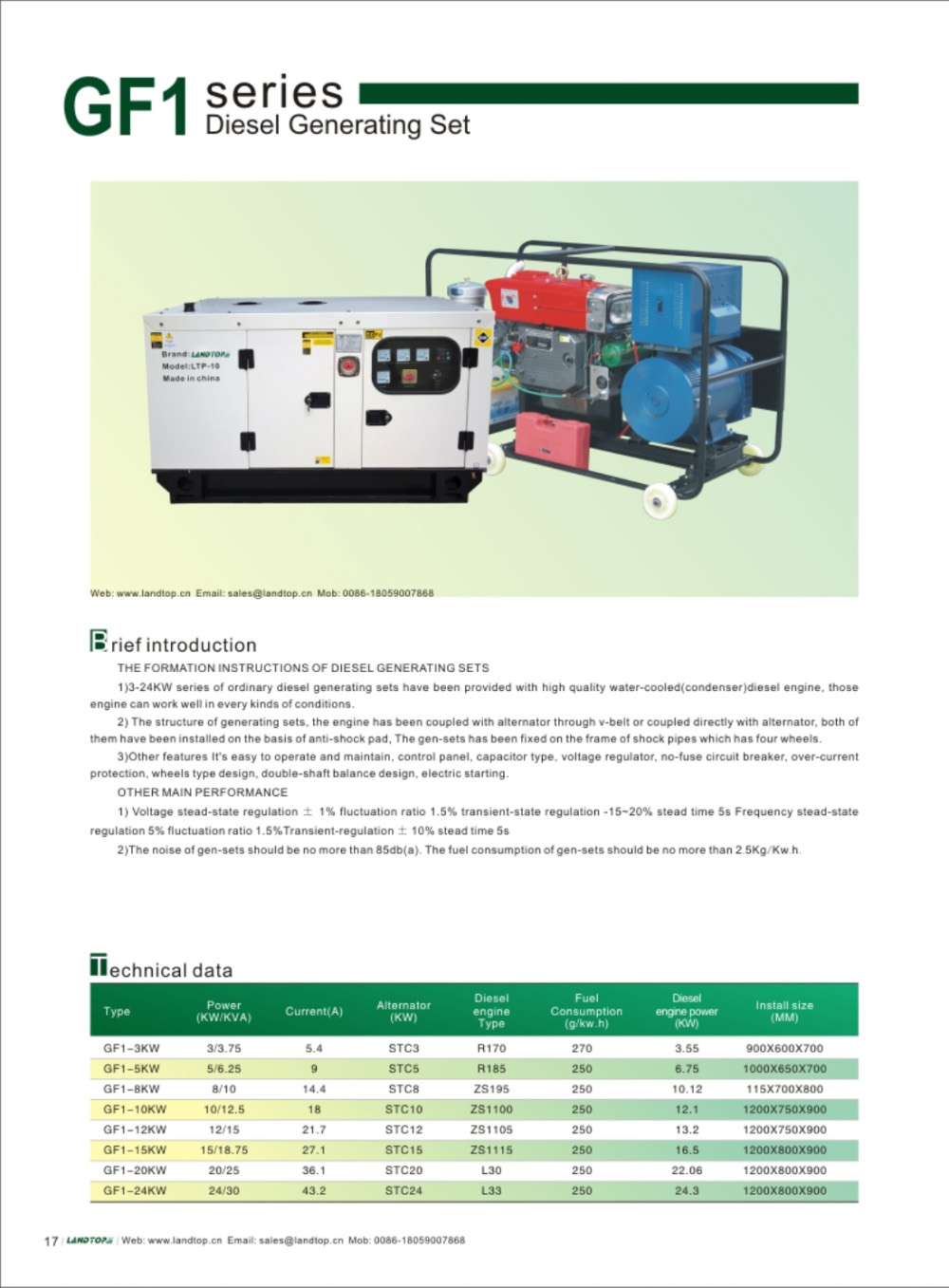
GF1 Series Diesel Generator,GF1 Single Cylinder Diesel Generator,Single Cylinder Diesel Engine,Generator GF1 Series
FUZHOU LANDTOP CO., LTD , https://www.landtopco.com