Beryllium Copper In The Electronics And Telecommunications Industry

Beryllium Copper, commonly known as BeCu, plays a vital role in the electronics and telecommunications industries. It's estimated that approximately half of all Beryllium Copper produced is utilized in these sectors for manufacturing essential equipment such as telecommunication infrastructure machines, computers, and mobile phones. These devices allow us to stay connected and communicate efficiently. Its unique properties, including excellent conductivity and durability, make it indispensable in modern technology. Without Beryllium Copper, our ability to maintain constant communication would be severely compromised.
Table of Contents
- Applications of Beryllium Copper in Electronics
- BeCu Electrical Conductivity
- Grades of Beryllium Copper
- C17200 Beryllium Copper Heat Treatment Process
- Beryllium Copper Alloys Composition
- BeCu Mechanical Properties
- Cryogenic Temperatures Properties of Berylco 25
- Beryllium Copper Alloys Physical Properties
- Applications of Beryllium Copper in Telecommunications
C17200 beryllium copper is used in fiber optic cables
The C17200 grade of Beryllium Copper is extensively used in fiber optic cables due to its impressive characteristics. These features ensure smooth functionality and long-term reliability. High tensile strength: This alloy exhibits excellent tensile strength, thanks to precipitation hardening, enabling it to withstand extreme bending pressures without deformation.
- Superior electrical conductivity: It offers remarkable electrical conductivity, making it ideal for handling high current applications.
- Formability: As an age-hardening material, it can be molded into intricate shapes with ease. Post-stamping or molding, it requires no additional heat treatment, providing a perfect balance between strength and formability.
- Outstanding fatigue strength: It demonstrates exceptional fatigue strength, which is crucial for components exposed to continuous rotational pressure.
- Corrosion resistance: Its superior corrosion resistance safeguards it from abrasive and harsh environments, ensuring prolonged lifespan.
- Heat resistance: It maintains its mechanical properties even under elevated temperatures, reducing performance degradation.
Applications of Beryllium Copper in Electronics

| Electrical | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fuse Clips | Electrical Switch / Relay Blades | Switch Parts |
| Relay Parts | Spring Connectors | Connectors |
| Contact Bridges | Current Carrying | Belleville Washers |
| Clips | Navigational Instruments | Â |
Beryllium copper alloy exhibit high strength, hardness and electrical conductivity
BeCu Electrical Conductivity
C (%IACS) = 1.7241/p20 x 100
where Ï20 (µΩ • cm) is the alloy's electrical resistivity at 20°C
| Berylco 14 & 8 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Before ageing | After standard ageing | Mill hardened |
| 22 to 25 % IACS | 45 to 48 % IACS | 45 to 65 % IACS* |
| Berylco 25 & 165 | ||
| Before ageing | After standard ageing | Mill hardened |
| 15 to 18 % IACS | 22 to 23 % IACS | 20 to 28 % IACS* |
Grades of Beryllium Copper
| Â | UNS C17200 | UNS C17510 | UNS C17000 | UNS C17500 | UNS C17300 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machinability rate | 20% | – | 20% | – | 20%. |
| Weldability |
|
|
|
|
|
| Forging temperature | 649 to 816°C (1200 to 1500°F) | 648 and 885°C (1200 and 1625°F) | 649 to 816°C (1200 to 1500°F) | 649 and 885°C (1200 and 1625°F) | 649 to 816°C (1200 to 1500°F) |
| Hot Working | Good | excellent | Good | good hot forming capacity | Good |
| Cold Working | Excellent | excellent cold working capacity | Excellent | excellent | Excellent |
| Annealing | 774 to 802°C (1425 to 1475°F) | – | 774 to 802°C (1425 to 1475°F) | – | 774 to 802°C (1425 to 1475°F). |
| Application |
|
|
|
|
|
CDA 172 beryllium copper is resistant to corrosion, radiation and heat
This alloy boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and is highly resistant to stress corrosion, making it superior to materials like brass or nickel silver. It also provides better corrosion protection than copper-nickel or aluminum bronze when exposed to seawater. Consequently, it is considered an ideal material where both corrosion resistance and mechanical strength are required simultaneously. An oxide layer forms on its surface during age hardening, acting as a protective coating. This enhances its resistance to high temperatures.
C17200 Beryllium Copper Heat Treatment Process
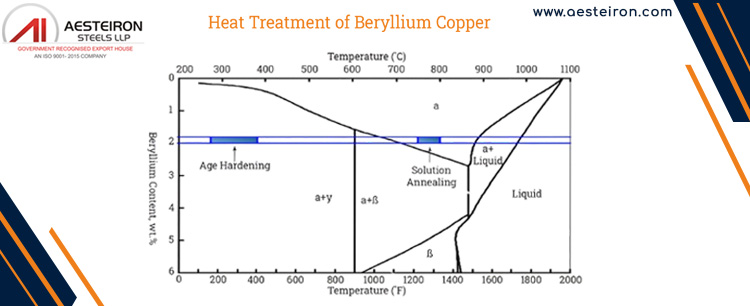
There are two main stages involved in the heat treatment process:
| 1] Solution Annealing | 2] Age precipitation |
|---|---|
|
|
Refer to the chemical composition and mechanical properties of BeCu alloy
Understanding its properties will help determine its suitability for various conditions. The following table provides comprehensive information about its mechanical and chemical characteristics. Its mechanical properties indicate high strength and excellent corrosion resistance.
Beryllium Copper Alloys Composition
| Alloys Designation | Â | High Conductivity | High Strength | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGK Berylco | B14 | B8 | B7 | B25 | B33/25 | B165 | |
| UNS | C17510 | C17510 | C17530 | C17200 | C17300 | C17000 | |
| ISO/ EN Symbol | CuNi2Be | CuNi2Be | CuNi2Be | CuBe2 | CuBe2Pb | CuBe1.7 | |
| ISO/ EN Number | CW110C | CW110C | CW110C | CW101C | CW102C | CW100C | |
| Chemical Composition | Beryllium (Be) | 0.2-0.6 | 0.2-0.6 | 0.2-0.4 | 1.8-2.0 | 1.8-2.0 | 1.6-1.8 |
| Cobalt (Co) | – | – | – | 0.3 max | 0.3 max | 0.3 max | |
| Nickel (Ni) | 1.8-2.5 | 1.4-2.2 |  | – | – | – | |
| Ni+Co | – | – | 1.8-2.5 | – | – | – | |
| Co+Ni+Fe | – | – | – | 0.6 max | 0.6 max | 0.6 max | |
| Lead (Pb) | – | – | – | – | 0.2 min | – | |
| Al | – | – | 0.6 max | – | – | – | |
| Cu | 99.5 min | 99.5 min | 99.5 min | 99.5 min | 99.5 min | 99.5 min | |
BeCu Mechanical Properties
| Â | UNS C17200 | UNS C17510 | UNS C17000 | UNS C17500 | UNS C17300 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Rockwell B) | 80.0 – 85.0 | 35 | 60 | 35 | 6 |
| Tensile strength | 1280 – 1480 MPa | 310 MPa | 483 MPa | 310 MPa | 469 MPa |
| Yield strength | 965 – 1205 MPa | 172 MPa | 32100 – 170000 psi | 172 MPa | 145000 – 175000 psi |
| Elongation | 15.0 – 30.0% | 28% | 45% | 28% | 48% |
C17510 BeCu has a conductivity rating of 15-30%
While not as conductive as pure copper, it remains an excellent conductor. Its remarkable strength and hardness make it highly sought-after for applications requiring high thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cryogenic temperatures properties of Berylco 25
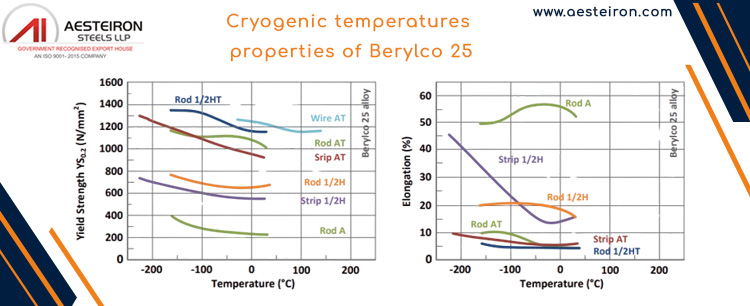
| Solution annealed and precipitation hardened | YS 0.2 (N/mm²) | UTS (N/mm²) | Young Modulus E (N/mm²) | A% on 25mm (%) | Charpy Impact (N/mm²) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature in °C | – 100°C | 1080 | 1380 | 131000 | 8 | 6.9 |
| – 200°C | 1170 | 1490 | 134000 | 9 | 9.6 | |
| 20°C | 980 | 1340 | 123000 | 5 | 5.5 | |
| – 150°C | 1110 | 1400 | 131000 | 9 | 8.3 | |
Beryllium Copper Alloys Physical Properties
| Physical properties after precipitation hardening | Specific heat | Melting point | Electrical resistivity p (maxi) | Coefficient of linear expansion | Density | Thermal conductivity | Modulus of elasticity | Fatigue resistance | Electrical conductivity | Magnetic permeability | Modulus of rigidity | Poisson’s ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Cal/(g.°C)) | (C) | (10â»â¸ Ω.m) | (x10â¶/°C) | (g/cm³) | (W/m.K) | (N/mm²) | (N/mm²) | (%IACS) | (μ=1+4) | (N/mm²) | ||
| (Cal/(g.°C)) at 20°C |  | .m at 20°C | at 20° to 200°C | at 20°C | at 20°C |  | at 10 cycles | at 20°C | (μ=1+4) |  |  | |
| B165 | 0.1 | 890-1000 | 7.8 | 17.5 | 8.35 | 90-135 | 128000 | 300 | 25 | 1.000042 | 49000 | 0.3 |
| B25 B33/25 | 0.1 | 865-980 | 7.9 | 17.3 | 8.26 | 84-130 | 130000 | 300 | 25 | 1.000042 | 50000 | 0.3 |
| B8 | 0.1 | 1005-1070 | 3.1 | 17.6 | 8.75 | 167-260 | 132000 | 240 | 63 | 1.000031 | 52000 | 0.3 |
| B14 | 0.1 | 1030-1070 | 3.8 | 18 | 8.75 | 167-260 | 132000 | 240 | 50 | 1.000031 | 52000 | 0.3 |
| B7 | 0.1 | 1050-1085 | 5.4 | 17.6 | 8.71 | 148-194 | 127000 | 250 | 38 | 1.000027 | 49000 | 0.3 |
Applications of Beryllium Copper in Telecommunications

| Telecommunication | |
|---|---|
| Connectors and Contacts | For reliable signal transmission and durability |
| Switches and Relays | Excellent conductivity and wear resistance |
| Heat Sinks | Manage heat in electronic devices |
| Shielding | Offers efficient electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding |
| Spring Contacts | For longevity in circuit boards |
| Grounding | Reducing electrical noise and improving safety |
| Terminals and Clips | Secure electrical connections |
Dual Temperature Zone Wine Cooler
Dual Temperature Zone Wine Cooler,Dual Zone Wine Cooler,Dual Temperature Wine Cooler,Temperature Wine Cooler
Guangzhou wanbao group refrigerator Co. Ltd. , https://www.wanbao-refrigerator.com