# Introduction to 300 Series Austenitic Stainless Steel
When it comes to materials science, stainless steel has long been a cornerstone of modern engineering. Among its many variations, the 300 series austenitic grades stand out for their exceptional combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. These alloys, especially grades 304 and 316, have become benchmarks within the industry, celebrated not only for their durability but also for their ability to adapt to a variety of applications.
## The Building Block of Stainless Steel: Chromium
Chromium plays a pivotal role in the creation of stainless steel. This critical element, which typically constitutes at least 10% of the alloy’s composition, is responsible for the material’s hallmark resistance to rust and corrosion. When exposed to air, chromium forms a thin, invisible layer that acts as a shield against environmental elements that could otherwise cause damage over time.
## 304 Stainless Steel: The All-Rounder
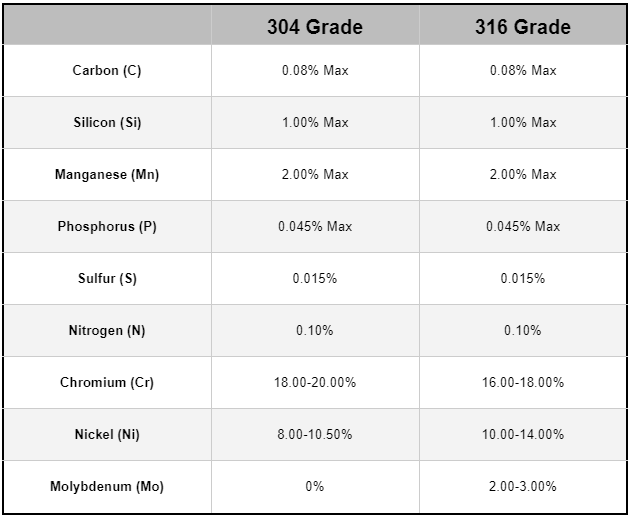
Grade 304 stainless steel, the most prevalent in the 300 series, is renowned for its adaptability and dependability. With 18% chromium and 8% nickel (commonly known as 18/8 stainless), this alloy boasts impressive corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Its widespread use spans from kitchen utensils to structural frameworks, proving its value across multiple sectors.
## 316 Stainless Steel: The Saltwater Warrior
Taking corrosion resistance up another notch is 316 stainless steel, which includes molybdenum in its makeup. Featuring 16% chromium, 10% nickel, and 2% molybdenum, this grade is engineered specifically to thrive in environments with high salinity or chloride exposure. Its superior performance in marine settings, chemical plants, and pharmaceutical facilities underscores its importance in demanding industries.
## A Side-by-Side Comparison: 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel
Both 304 and 316 stainless steels excel in their respective domains. While 304 is ideal for general purposes where typical corrosion resistance is sufficient, 316 shines in situations involving aggressive chemicals or chloride-heavy conditions. The addition of molybdenum in 316 provides enhanced protection against pitting and crevice corrosion, making it the preferred choice for challenging environments.
## Welding and Forming Abilities
One of the standout features of both 304 and 316 stainless steels is their ease of welding and forming. This flexibility allows them to be shaped into intricate designs, a trait that has made them favorites in diverse industries. Although these alloys cannot be hardened through heat treatment, they gain significant strength through cold working. Variants like 304L and 316L, with lower carbon content, offer an excellent balance of weldability, corrosion resistance, and formability, making them suitable for numerous industrial and construction projects.
## Versatile Applications Across Industries
The uses of 304 and 316 stainless steels extend far beyond the ordinary. Grade 304, with its 18% chromium and 8% nickel content, finds extensive application in kitchen appliances, sinks, and architectural panels due to its robust corrosion resistance and formability. It works well in environments where it will encounter a broad spectrum of organic and inorganic substances, though it may not be the best option for highly saline or chloride-exposed areas.
Conversely, Grade 316 stainless steel, enriched with 2-3% molybdenum, offers heightened corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and marine conditions. This makes 316 the go-to material for marine applications, chemical processing systems, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and even medical implants. Despite being pricier than 304, 316's superior performance under harsh conditions often justifies the added expense.
## Super Austenitic Grades: Elevating Performance
Moving beyond the standard 304 and 316 grades, the super austenitic variants within the 300 series deliver enhanced performance tailored for extreme conditions. These high-nickel alloys boast superior corrosion and oxidation resistance, making them indispensable for applications requiring unparalleled strength and resilience.
## Composition of Austenitic Stainless Steel
The exact composition of austenitic stainless steel varies depending on the specific grade, but chromium and nickel remain the primary components that define its characteristics. Understanding these compositions helps engineers select the right material for particular applications.
## Frequently Asked Questions
### Q1: What gives 304 and 316 stainless steel their corrosion-resistant properties?
A1: Their corrosion resistance stems from chromium, which creates a protective oxide layer. In 316 stainless steel, molybdenum further strengthens this resistance, particularly in chloride-rich settings.
### Q2: How does molybdenum improve 316 stainless steel?
A2: Molybdenum significantly bolsters 316's resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly beneficial in saline or chloride-prone environments, ensuring durability in tough conditions.
### Q3: What distinguishes super austenitic grades from 304 and 316?
A3: Super austenitic grades feature elevated nickel levels, offering superior corrosion and oxidation resistance. They cater to extreme environments and applications needing heightened strength and resilience compared to standard 304 and 316 grades.
Whether you're looking for fittings, flanges, tubing, or specialized components, stainless steel remains a reliable choice for countless industrial needs. Investing in high-quality stainless steel products ensures longevity and performance, whether you're building a kitchen appliance or constructing a marine vessel.
Pulleys
Herringbone Pulley,Herringbone Belt,Drive Belt Pulley,Belt Conveyor Drive Pulley
NINGBO TANSUO MACHINE MANUFACTURING CO., LTD. , https://www.tsjxidler.com