Kjeldahl method for measuring ammonia nitrogen in feed
Ammonium nitrogen (NH3N) is present in silage in the form of free ammonia (NH3) or ammonium salt (NH4+). The composition ratio of the two depends on the pH of the silage. When the pH is high, it exists in free form. It exists as an ammonium salt. 2以下。 Silage well-preserved conditions is a pH of 4.2 or less. The ammonia nitrogen in the good quality silage exists as an ammonium salt, but when the silage is heavily corrupted, it will smell a pungent ammonia smell. The ammonia nitrogen in the silage is mainly the decomposition product of nitrogen-containing organic matter by plant enzymes and aerobic bacteria, so the content of ammonia nitrogen can be used as an indicator of the degree of protein degradation in silage. The ratio of ammonia nitrogen to total nitrogen commonly used in the laboratory to reflect the fermentation quality of silage. At present, spectrophotometry and alkali distillation titration methods are mainly used for the detection of ammonia nitrogen in silage. Spectrophotometric method is widely used in the analysis of ammonia nitrogen, but due to the large toxicity of reagents and the metal ions, sulfides, aldehydes and ketones, color, etc. of calcium, magnesium, and iron in the extract, they all need to be pre-measured. deal with. The conventional semi-micro alkali distillation method is also a commonly used method, but due to the cumbersome operation and long measurement time, it is not suitable for analysis of a large number of samples. The purpose of this study was to investigate the determination of ammonia nitrogen in silage using an automated Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer to meet the needs of silage scientific research and quality control for simple, rapid, accurate, and large-volume sample testing.
1 Experimental principle The Kjeldahl method is mainly used to determine the content of organic nitrogen in a sample. The principle is that the sample is digested with concentrated sulfuric acid under the action of a catalyst, and the protein and other organic nitrogen therein are converted into NH4+ and generated with sulfuric acid (NH4). ) 2SO4. The digestive liquid is distilled under the action of concentrated alkali, ammonia is released, absorbed by boric acid solution and combined with it to form ammonium tetraborate, and then titrated with hydrochloric acid.
The ammonia nitrogen in the silage mainly exists in the form of ammonium salt. The ammonium salt and ammonia stronger alkali distill out ammonia under the condition of heating together. In this study, automatic Kjeldahl determination of ammonia nitrogen in silage is used. The principle is that ammonium salt is easily soluble in water. In the experiment, the sample is directly digested without water to prepare an extract. Magnesium oxide, magnesium oxide and water are slowly and slightly soluble. Magnesium hydroxide is then heated to distill ammonia out, automatically absorbed, titrated, and calculated.
2 Analysis 2.1 Selection of operating conditions of the instrument The method is the same as the principle of semi-micro determination of nitrogen. Both are used to distill out the ammonia and ammonium salts of the extract under alkaline conditions. Considering that the pH of the silage extract itself is low (around 4.0), the appropriate amount of water should be selected. Under the premise that the extract and magnesia are unchanged, the effect of different water addition on the determination result of ammonia nitrogen is shown in Table 1.
The results showed that the amount of water added had no significant effect on the test results, and the amount of water added during the measurement was chosen as 50 ml.
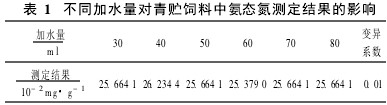
Table 1 Effect of different amount of water on the determination of ammonia nitrogen in silage 2.2 Effect of experimental operation It was found in the experiment that the extract should be measured immediately after adding magnesium oxide, otherwise the determination result will be due to the conversion of ammonium salt in the extract to ammonia volatilization. Low.
2.3 Standard recovery experiment The ammonia nitrogen in the silage is the basic nitrogenous substance such as ammonia and ammonium salt that the protein in the plant raw material decomposes during the process of spoilage, so this experiment will use ammonium sulfate as the standard reagent to test the recovery rate of the distiller. The standard recovery experiment was performed, and the recovery rate was between 99.8% and 104.3%, which met the testing requirements (see Table 2).
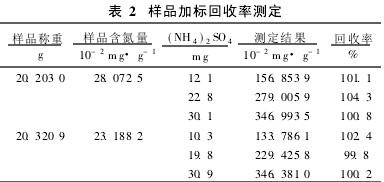
Table 2 sample determination of recovery rate 2.4 precision experiment precision experiment selected different silage fresh samples were measured in parallel for 6 times, the relative standard deviation of the measurement results were 139.9% and 0. 50% (see Table 3 ), the precision of the instrument determination method meets the analysis requirements.
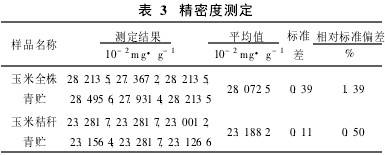
Table 3 Precision Determination 2.5 Comparison of Different Methods For the same sample, this method and manual semi-micro alkali distillation method were used to determine the content of NH3N. The results showed that there was no significant difference between the two methods (Table 4).
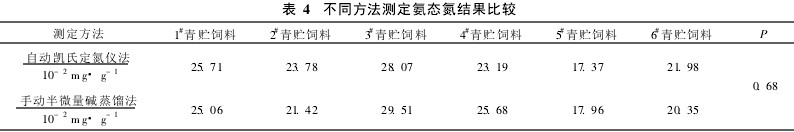
Table 4 Determination of ammonia nitrogen by different methods Comparison 3 Discussion (1) Experiments show that the automatic Kjeldahl nitrogen method and manual semi-micro alkali distillation method, by two-sample average t test analysis, no significant difference (P >0. 05). The automatic Kjeldahl method has the advantages of simple operation, high analysis speed and high degree of automation, and is suitable for the determination of large quantities of samples. After several parallel determinations and spike recovery experiments, the results show that the automatic Kjeldahl method has high accuracy, good repeatability, and high recovery.
(2) The preparation of the extract is influenced by the degree of homogeneity and oscillation time of the sample, so it should be shredded as much as possible and be shaken sufficiently to reduce the extraction loss.
(3) In this experiment, deionized water was used instead of redistilled water. The experimental data shows that the accuracy and precision of the detection can be satisfied, and the experimental water and energy consumption can be reduced, which is of practical significance.
Variable Regulating Valve,Temperature Controlled Water Valve,Double Regulating Valve,Air Reducing Valve
Galaxy Valve Co., Ltd. , http://www.tjgalaxyvalve.com